Ganglion Cyst Removal Surgery & Treatment in Dallas, Texas
What is a Ganglion Cyst?
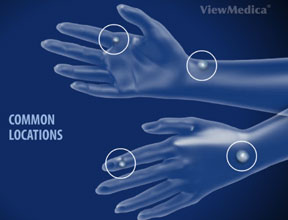
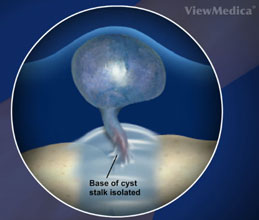
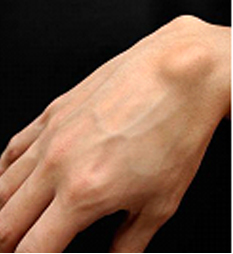
A ganglion cyst is a soft-to-firm, round growth located on the wrist joint. Usually about 1-3 cm in diameter, it is non-mobile. It can be found most commonly on the dorsal aspect of the wrist but can occur on the volar side as well. This benign growth is tethered to the wrist joint by a stalk known as the pedicle. Less frequently, the pedicle may anchor the ganglion cyst to a flexor tendon in the wrist. The fluid contained within the walls of the cyst is thick and gelatinous and is structurally different from the synovial fluid found in other joints. It is not associated with any underlying inflammatory process.
In some cases, a smaller ganglion cyst is nestled between the wrist joint and overlying tissues. Because of its size and covert location, this type of ganglion cyst may not be visible with the naked eye. A high degree of suspicion from an experienced clinician is needed to search for these occult ganglion cysts.
What Causes a Ganglion Cyst?
The true cause of a ganglion cyst is unknown. Some speculate that a genetic predisposition of underlying connective tissues can contribute to the frequency of occurrence. Another likely explanation asserts that trauma or repetitive movement in the wrist causes injury. Injury causes a defect in the wrist joint which allows leakage of synovial fluid from the joint into the tissues that surround the wrist. The cells present in this area react with the synovial fluid to create the gelatinous material of the cyst, which is then walled off by the body, forming the ganglion cyst capsule and pedicle.
What are the Symptoms of a Ganglion Cyst?
Ganglion cysts are space occupying lesions and as such may cause variable amounts of discomfort or pain depending on size or location. Pain, if present, tends to be a constant, annoying, dull ache that may radiate up the arm. Ganglion cysts may be large enough to interfere with the range of motion of the wrist. If tethered to a flexor tendon, it may interfere with grip strength or movement of the associated fingers. A frequent complaint with dorsal ganglions is pain when extending the wrist such as pushing off from a seated position, doing a push up or a plank position in yoga.
How is a Ganglion Cyst Diagnosed?
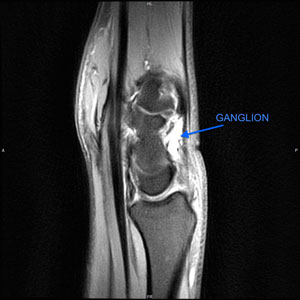
A thorough history and physical exam are important tools that aid in diagnosis. In more complicated presentations, ultrasound may be used to confirm that the growth is indeed filled with fluid, and not a solid mass of other origin. If the mass is cystic, therapeutic needle aspiration may be employed to remove the contents of the cyst to confirm a ganglion cyst. MRI is used to look for smaller, occult ganglion cysts not visible with the naked eye. MRI may be needed to plan for surgery, especially in cases where the ganglion cyst is thought to be attached to an underlying tendon, or the symptoms mimic other conditions such as Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. MRI does have its limitations. Sometimes an MRI may not detect a ganglion cyst, and for these reasons, surgery is the best method for both diagnosis and treatment of a ganglion cyst. Once the cyst is removed, it can be sent to a pathologist for confirmation of the diagnosis.
How is a Ganglion Cyst Treated?
Ganglion Cysts can be treated either non-surgically or surgically.
Non-Surgical
Watchful and waiting can be used once it is determined that a Ganglion Cyst is, indeed, present. It is estimated that 50% of ganglion cysts may resolve on their own, although recurrence is extremely common. In actuality, they may just become smaller to later enlarge as more fluid refills it. The best candidates for watchful waiting are those without pain whose main concern is the cosmetic appearance of the cyst.
Needle aspiration is often employed to remove the fluid from a ganglion cyst. Needle aspiration is oftentimes paired with the injection of a medication into the ganglion cyst. Again, recurrence is extremely common.
Surgical
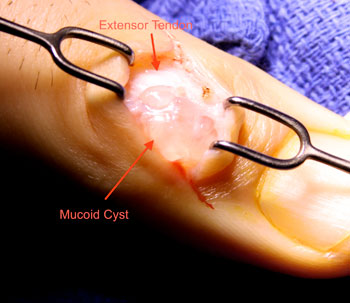
Although recurrence is possible with surgical removal of the ganglion cyst, the odds of recurrence are much lower, about 5%. Surgery is considered the best treatment option for those with painful ganglion cysts or cysts which interfere with the function of the wrist. Successful, permanent removal of ganglion cysts involves the removal of the cyst, its pedicle, and the margin of the joint capsule or tendon sheath where the pedicle attaches. If the surgeon fails to remove any of these aspects, the ganglion cyst has a higher chance of recurrence. For this reason it is strongly recommended that an experienced surgeon who focuses on the hand and the wrist be sought out for this procedure.
How can Dr. Knight help you with a Ganglion Cyst?
Ganglion cysts are one of the most common wrist ailments, and throughout his career as a surgeon Dr. Knight has treated countless occurrences. His experience allows him to comfortably recommend the best possible treatment for a Ganglion cyst, one that both fits the patient and the condition. Dr. Knight offers several Dallas, Texas locations to treat patients in need of cyst removal. You will find the entire process with Dr. Knight and the Hand and Wrist Institute staff to be professional from start to end. Dr. Knight is a specialist at Ganglion Cyst Removal with thousands of operations successfully completed. Come see us at either our Southlake, Texas office or Dallas, Texas office.
Ganglion Cyst Fact Sheet
| What can cause a person to develop a ganglion cyst? | The precise mechanisms that cause ganglion cysts to occur are not clearly understood, but the formation is brought about by loose synovial fluid in the open spaces of the wrist joint. |
| Can I treat my ganglion cyst without consulting a doctor? | There are no effective self treatments for ganglion cysts, the only truly effective way to treat the condition is through medical intervention. |
| Medications for Ganglion Cyst | There are no medications available |
| Can Ganglion Cysts be permanent? | Yes and no. They may come and go without any pattern over the course of time. |
| Treatment for Ganglion Cysts | Needle aspiration to remove the fluid from the cyst or surgery to remove the whole cyst |
| Can I pop the cyst? | You can, but it is not advisable. The fluid in side the cyst will not go away, simply reenter the open spaces of the bones of the wrist, and this will cause another cyst to grow, either very soon or in time. There is no way to determine exaclty how long it may tak a cyst to grow, but it definitely will. |
| Are Ganglion Cysts cancer? | No, this particular type of tumor is always benign. |
Frequently Asked Questions:
Are Ganglion Cysts dangerous?
Ganglion Cysts are a lot of things: uncomfortable, unsightly, irritating and mysterious. But one thing they are not is dangerous. In most cases, they simply crop up and disappear with very little rhyme or reason, and while they can cause discomfort and, on occasion, limit range of motion and wrist flexibility, they do not present a danger or threat to the overall health of the patient.
Can a Ganglion Cyst be malignant?
While a Ganglion Cyst might present in a similar way to a tumor, they are something entirely different, and because of the distinct difference in composition in cancerous tumors and cysts, Ganglion Cysts are not, and cannot be, cancerous.
Why do Ganglion Cysts sometimes go away on their own?
Just as doctors aren’t entirely sure what causes Ganglion Cysts to occur in the first place, we likewise don’t understand the precise mechanisms that cause them to go away, often just as quickly and mysteriously. Despite being one of the most commonly treated conditions of the wrist and hand, the continued mystery of what causes Ganglion Cysts continues to vex doctors.
What is inside a Ganglion Cyst?
A Ganglion Cyst is filled with a clear, viscous, and sticky fluid known as synovial fluid. This is essentially the same fluid that lubricates the joints in our body and may be indicative of a possible cause of the Cyst in the first place.
Can’t I just bang it with a bible?
You CAN, but it is not advisable. By bursting the cyst within the wrist joint, you are simply displacing the synovial fluid that fills it, and it will find another place to adhere itself and form another cyst. This is why surgical removal or aspiration are much better options.
Ganglion Cyst Videos
See Dr. Knight discuss his protocol for ganglion cysts. Click on video.
Animated Videos
Surgical Videos
Note: The following videos contain graphic images.
(817) 382-6789
Disclaimer
HandAndWristInstitute.com does not offer medical advice. The information presented here is offered for informational purposes only. Read Disclaimer